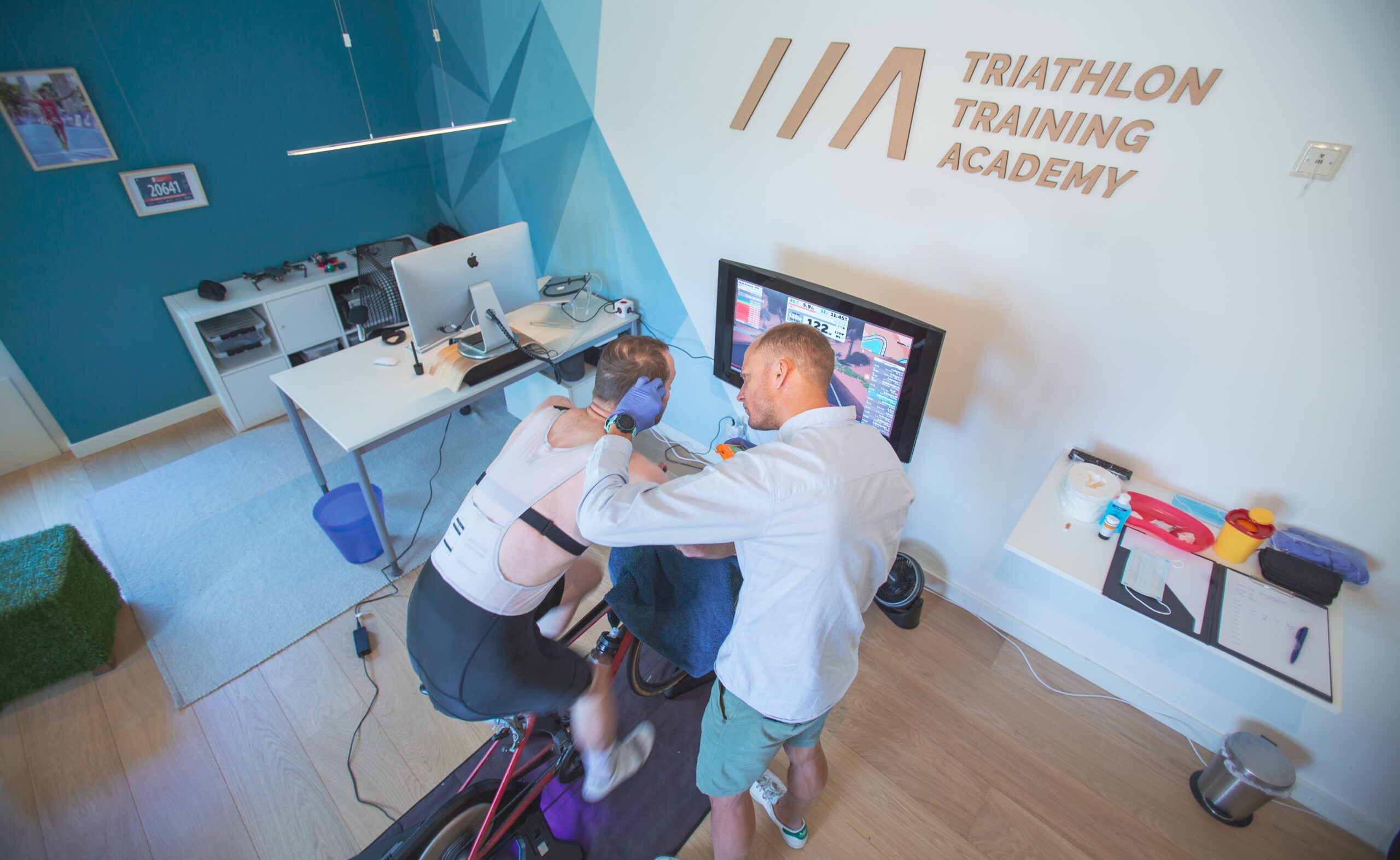
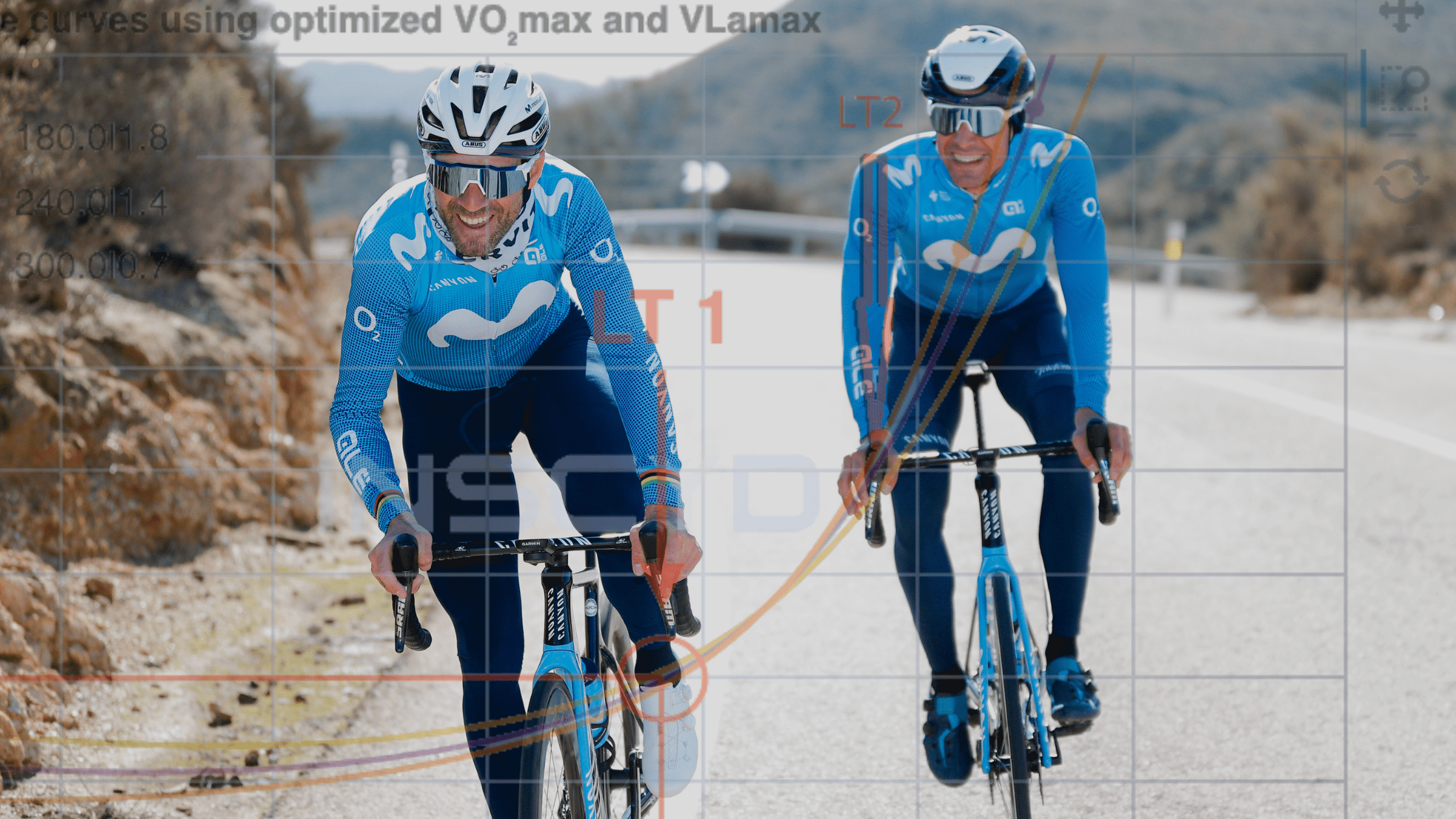
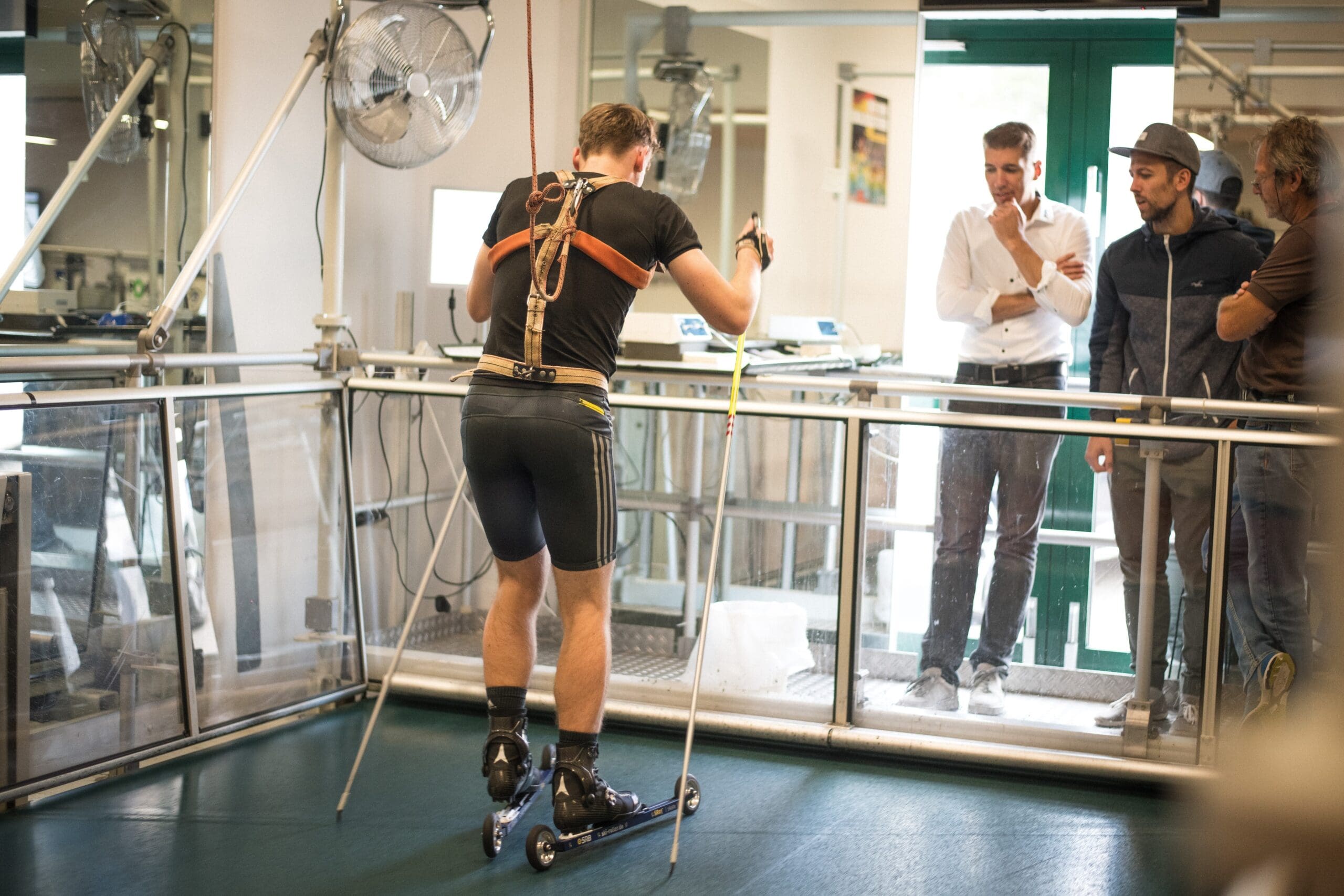
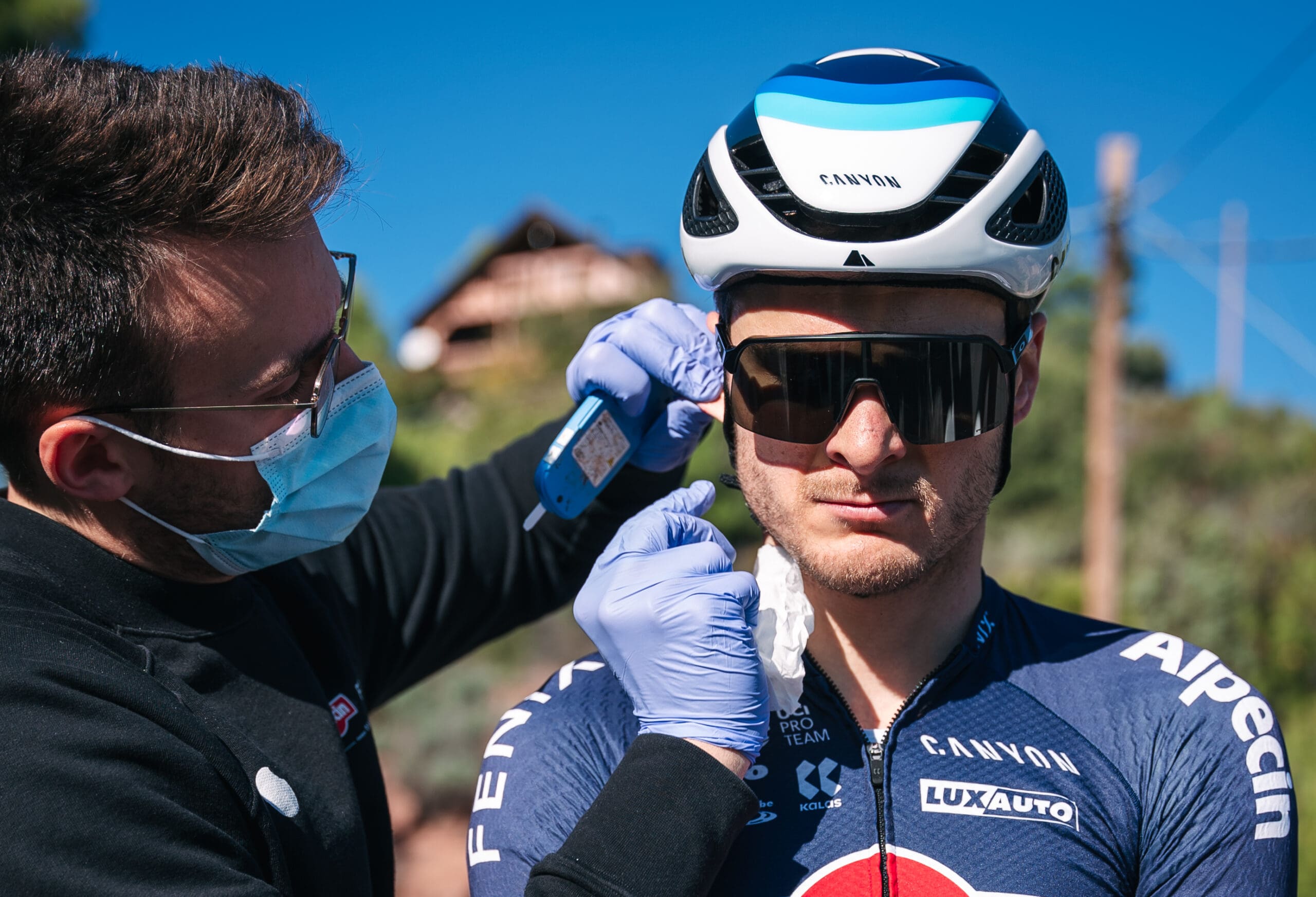
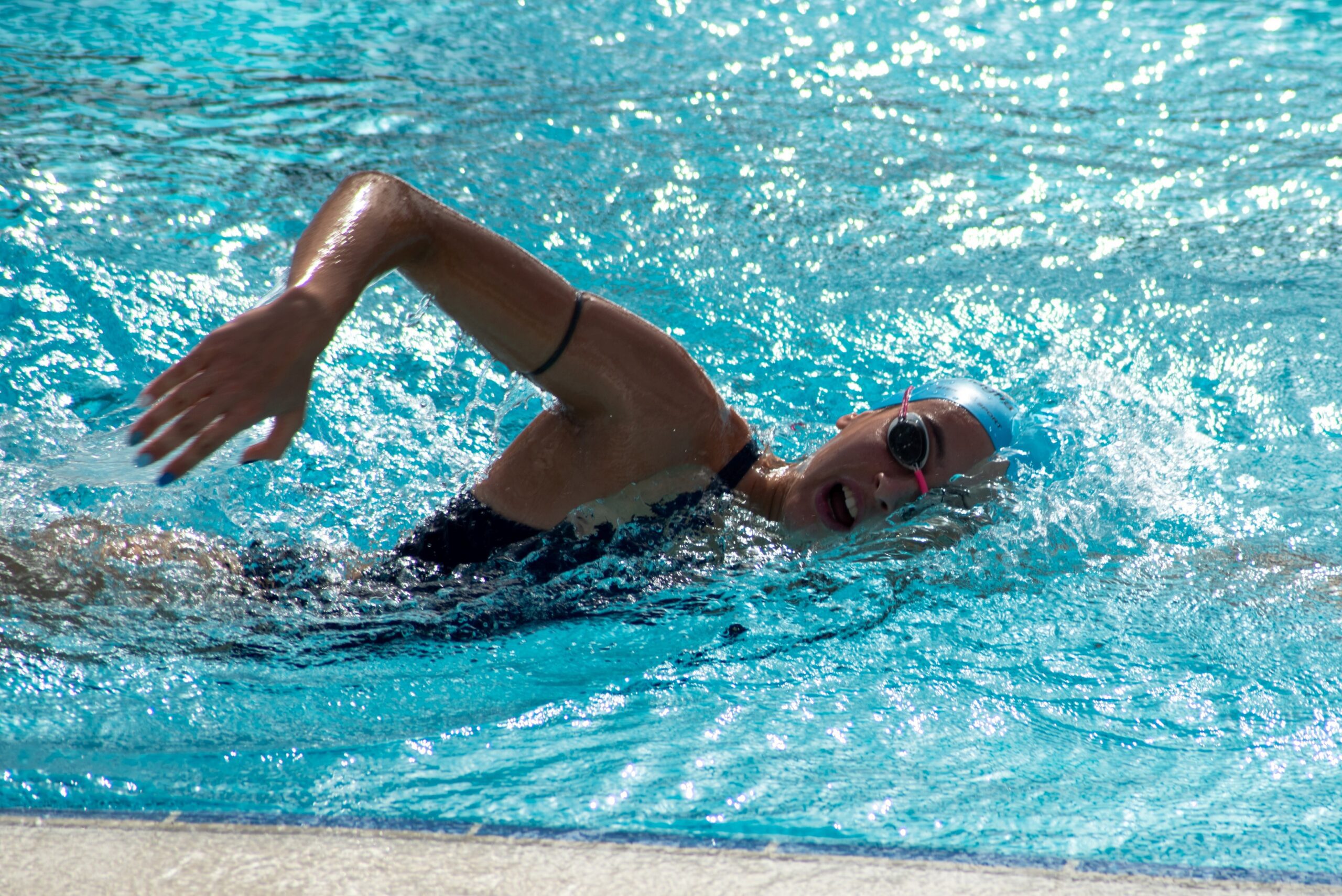
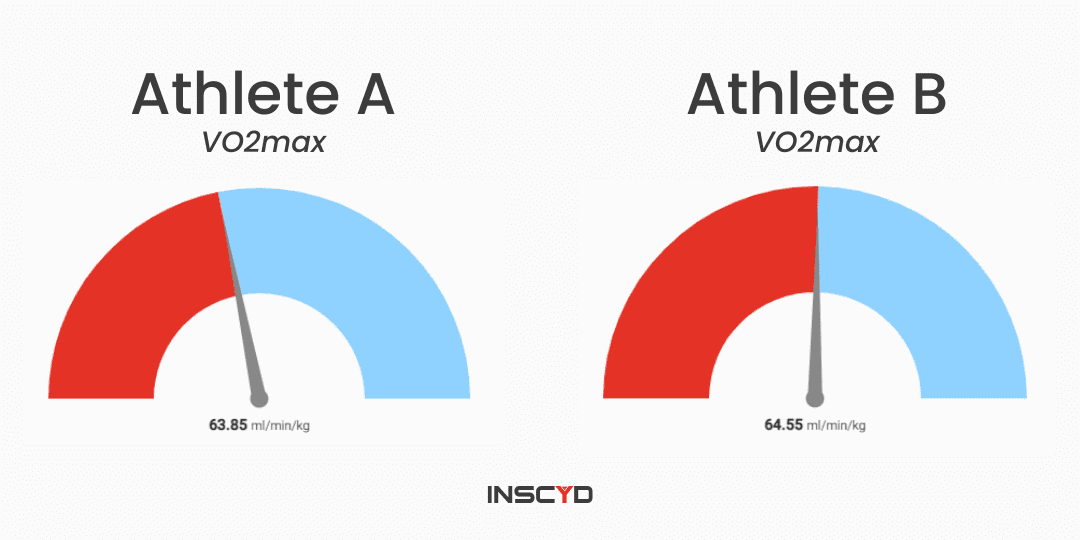
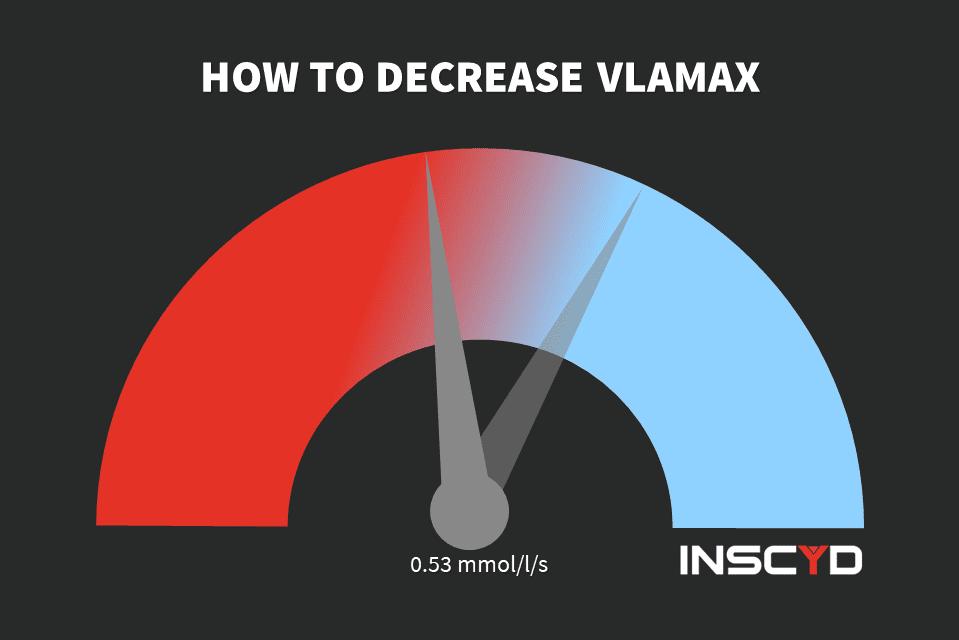
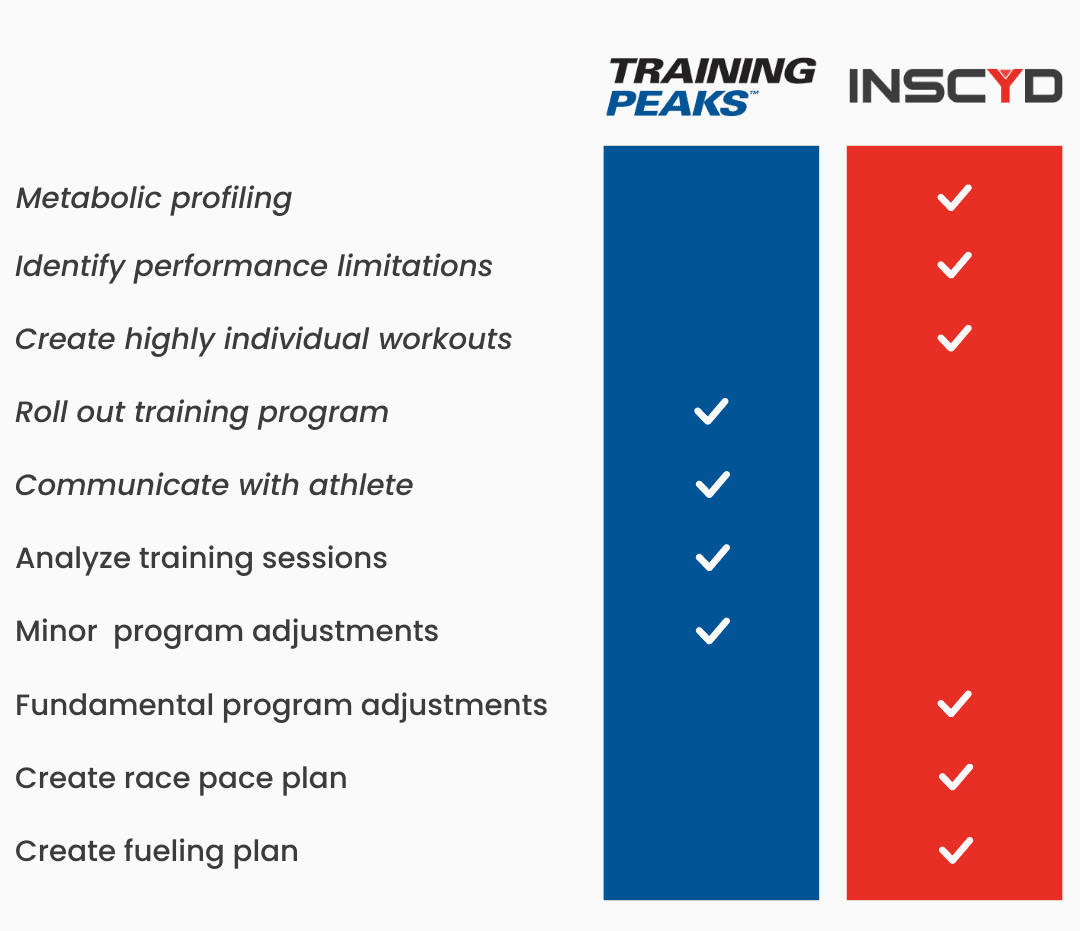
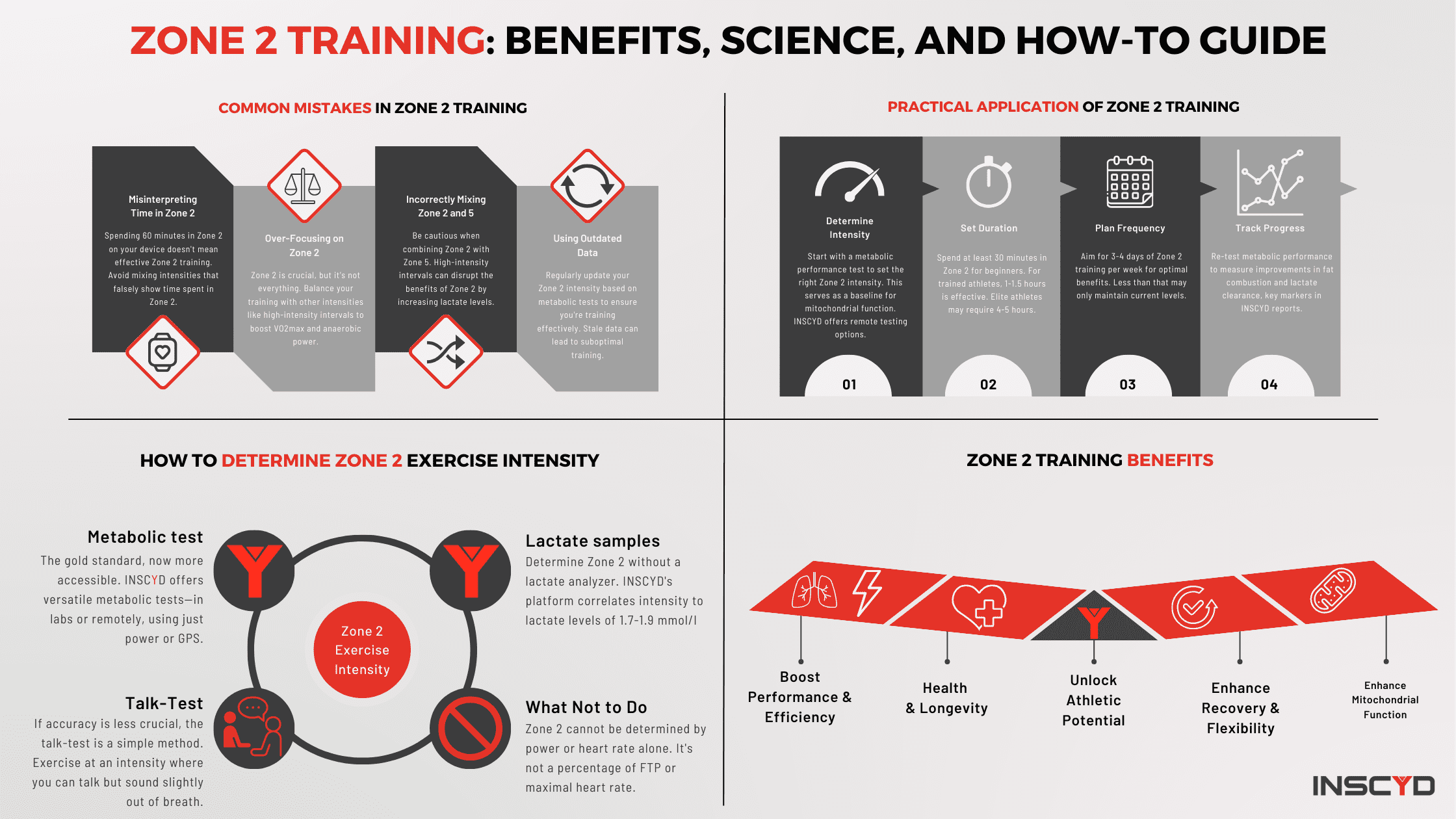
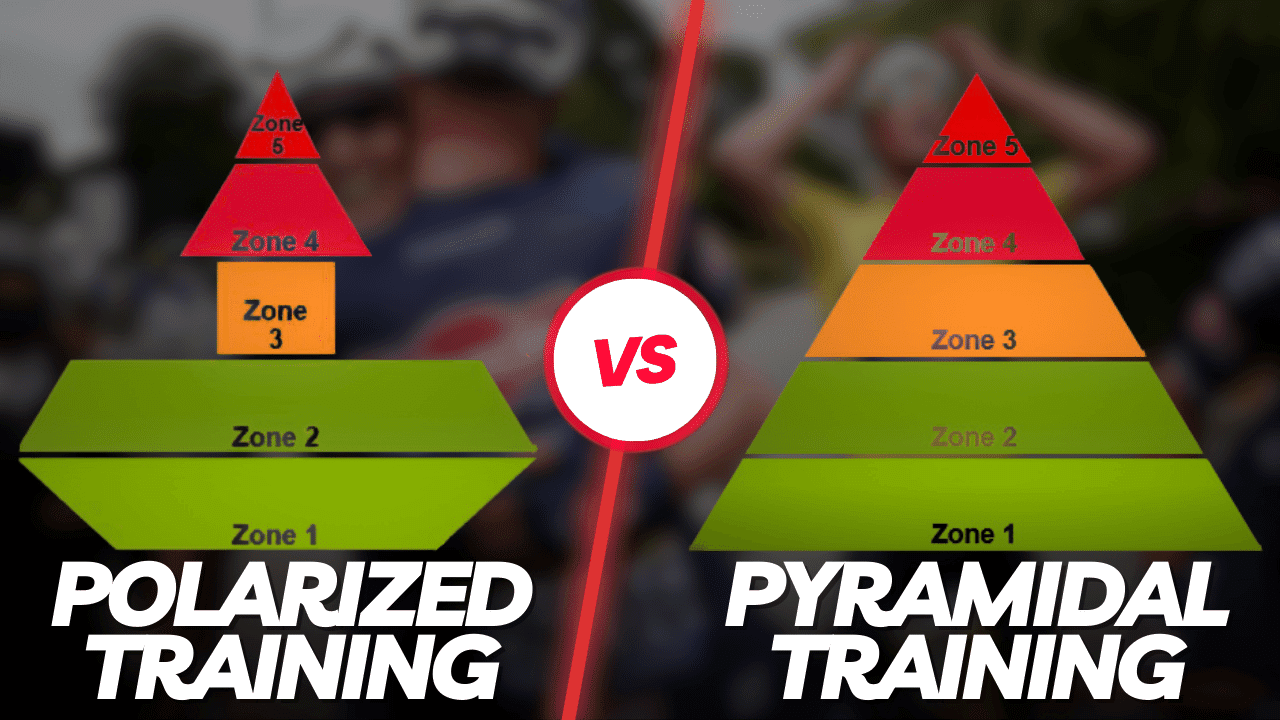
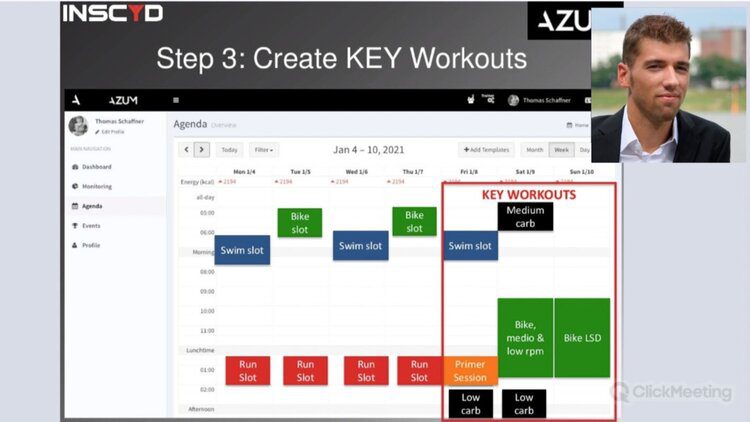
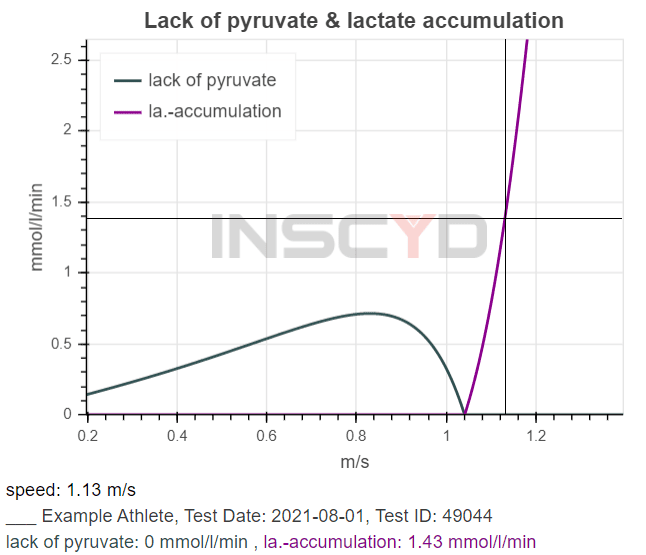
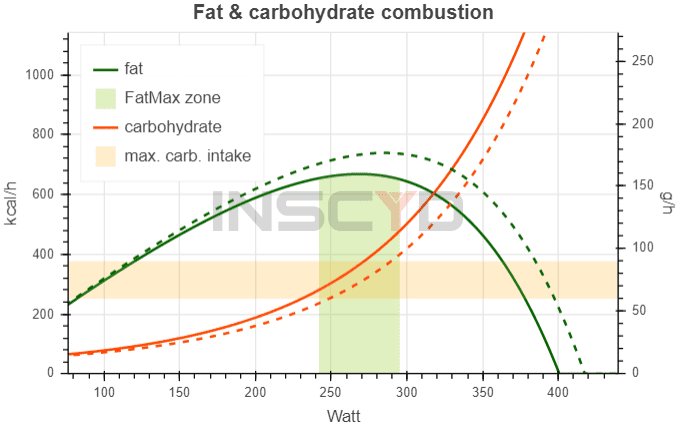
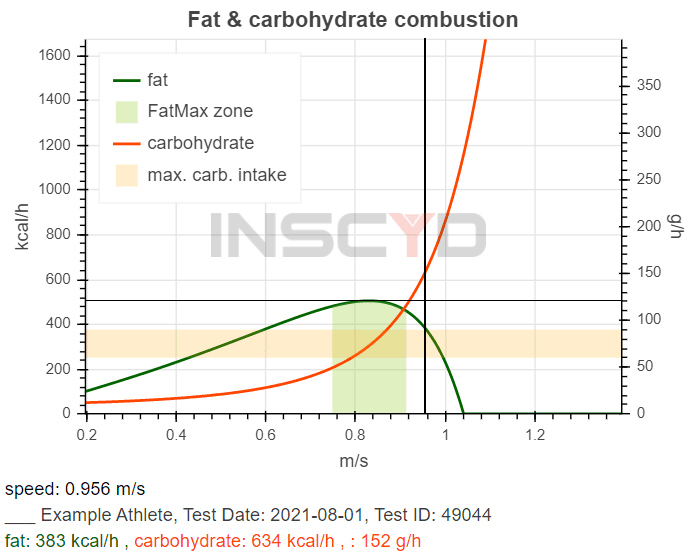
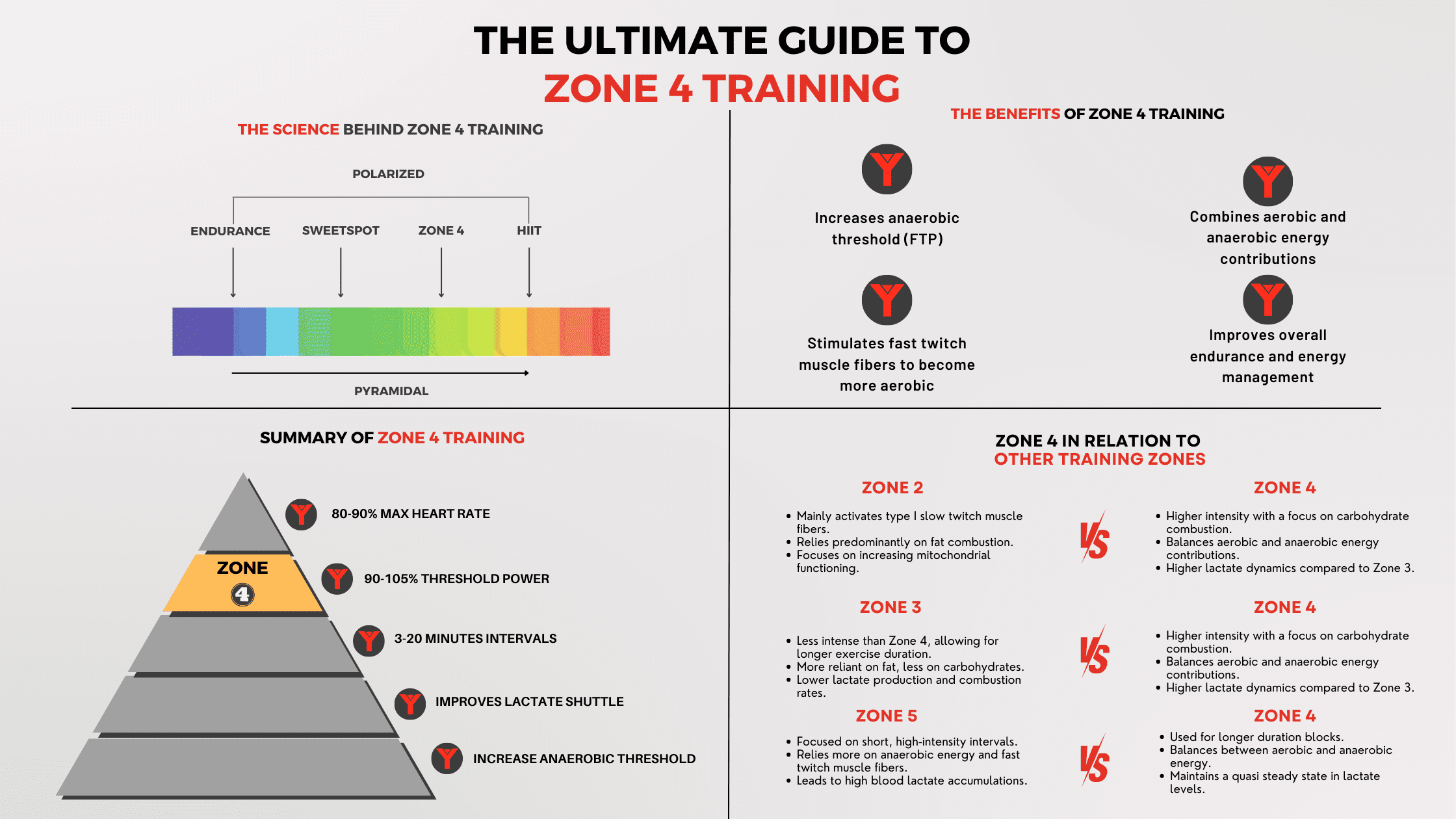
Individualize race preparation based on athlete’s unique metabolic profile
The last weeks prior to an important race event are crucial. Use the wrong training strategy, and all the hard work is lost. Manage your training the right way and you’ll boost your performance by a few percent. In this use case, Benjamin Tilus, National Champion Coach and Founder of XLR8 Performance Lab, shares how to…